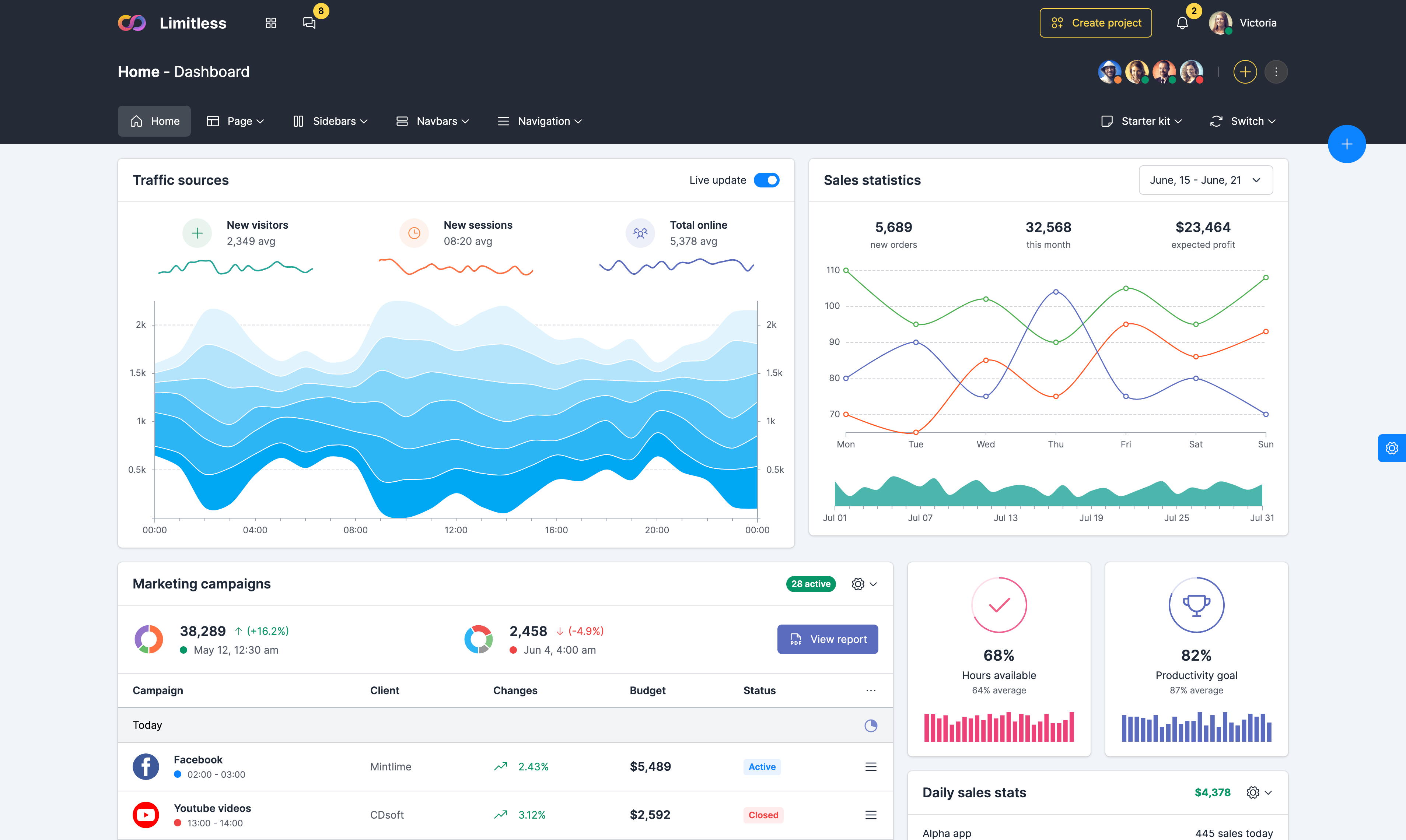
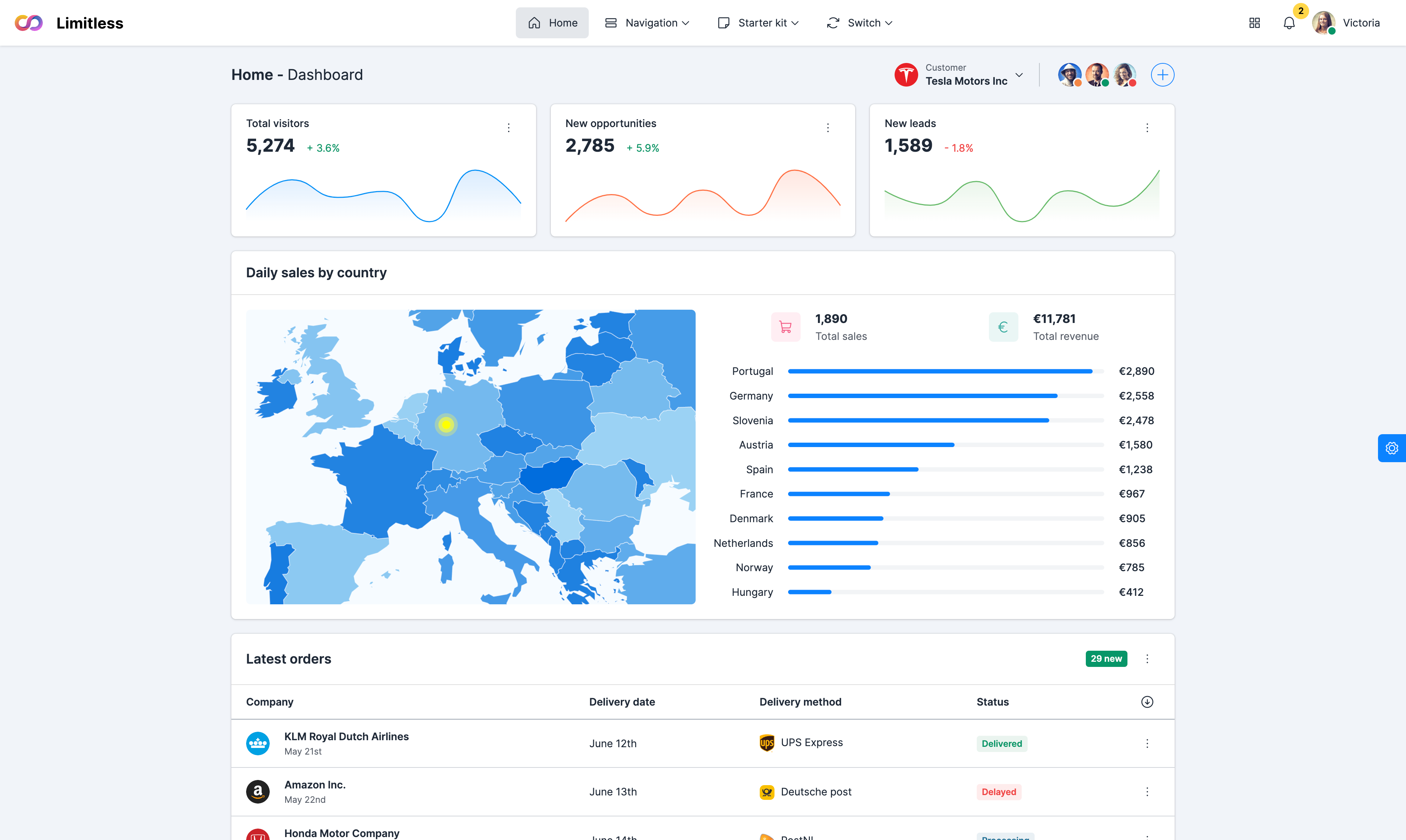
Navigation
-
Main
- Dashboard No pending orders
- Layouts
- Themes
- Starter kit
- Changelog 4.0
-
Forms
- Form components
- Text editors
- Pickers
- Form layouts
-
Components
- Basic components
- Content styling
- Extra components
- Color system
- Animations
- Icons
-
Layout
- Page layouts
- Sidebars
- Navbars
- Vertical navigation
- Horizontal navigation
- Menu levels
-
Data visualization
- Echarts library
- D3 library
- C3 library
- Google charts
- Maps integration
-
Extensions
- Extensions
- File uploaders
- Event calendars
- Internationalization
-
Tables
- Basic tables
- Grid.js tables
- Data tables
- Data tables extensions
-
Page kits
- General pages
- Service pages
- User pages
- Application pages
- Widgets
Custom components
Besides navigation, navbar component supports custom content such as: dropdowns with submenu, dropdown menus with custom content, full width dropdowns, language selection, forms, tabs, multi level menus, date pickers etc. Everything is adapted to use in different navbar color schemes and sizes. Examples below demonstrate some of these components, other examples related to mega menu can be found on this page.
Navbar navigation
Basic navigation
Navbar navigation links build on our .nav options with their own modifier class and require the use of toggler classes for proper responsive styling. Navigation in navbars will also grow to occupy as much horizontal space as possible to keep your navbar contents securely aligned. Dropdown menus require a wrapping element for positioning, so be sure to use separate and nested elements for .nav-item and .nav-link.
Navigation icons
Navbar navigation supports icons: text with left and right positioned icons, multiple icons within 1 item, icons only and carets for items with dropdown menu. By default, sidebar control buttons are placed in the left navigation. To add icons, place <i> element with icon class to the navigation link element. To use with text, depending on the position place icon before or after item text. Use .ms-2 or .me-2 to add left/right spacer between the icon and nav link text.
Badges
Flexibility of the navbar navigation also allows you to use 2 kinds of badges - inline and floating. Both types can have left and right positions. To use inline badge, just add badge markup next to the text label, default placement is absolute with top-right position. To use left positioned elements, place it before text in inline version and use our utility classes to adjust position.
Badge marks
Instead of badges, which should contain text by default, navbar component supports badge marks - small rounded indicators. These indicators support all available colors and can have 2 different styles - circle and ring. To use ring, use a combination of our border, background and padding utility classes. Colors are controlled by color classes without any additional CSS. Both variations do not require .badge class by default. Also these indicators support left/right alignment and static/absolute positioning.
Basic components
Navbar buttons
Various buttons are supported as part of navbar components. This is also a great reminder that vertical alignment utilities can be used to align different sized elements. Button groups and button dropdowns in different colors, sizes and styles are also supported. For multiple buttons, use reponsive spacing utility classes for proper vertical and horizontal alignment.
Navbar text
Wrap strings of text in an element with .navbar-text, usually on a <span> tag for proper leading and color. This class adjusts vertical alignment and horizontal spacing for strings of text. In some cases links within .navbar-text may need color adjustments, use color utility classes to style links properly.
Progress bars
Provide up-to-date feedback on the progress of a workflow or action with simple yet flexible progress bars. Progress bars inside navbar support all possible styling options: colors, animations, labels, appearance, sizes etc. Also you can add text and icon labels to display current action, it's also available in both left and right positions.
Form components
Place form content within container with spacing utility classes for proper vertical alignment and collapsed behavior in narrow viewports. Use the alignment options to decide where it resides within the navbar content. Navbar supports all form components: checkboxes, radios, default and custom selects, file inputs etc. Some form controls, like input groups, may require width utility classes to be show up properly within a navbar.
Input group, file select


















 España
España
 English
English
 Українська
Українська
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 IT
IT